1. Calculator
2. Supported chemical formula formats
3. Batch calculation
4. Element information
5. Plot
6. Additional literature
7. Supported browsers
1. Calculator
The landing page allows real-time calculation of the effective elemental scarcity - ζ (crustal abundance in inverse ppm), Herfindahl−Hirschman Index production value - HHI (production), and Herfindahl−Hirschman Index reserves value - HHI (reserves) of compounds by provided chemical formula.
A chemical formula can be pasted, entered, or edited directly in the input field through the computer keyboard. It can be also entered through clicks on the elements of the periodic table keyboard (Figure 1). Multiple left clicks on the same element increase the stoichiometric coefficient of the selected element and right clicks decrease it. To edit a formula through the periodic table keyboard, place the cursor next to an element and click on its cell in the periodic table to increase or decrease its stoichiometric coefficient.
For example, to calculate the elemental scarcity of Li2O: On the periodic table keyboard Click twice on lithium (Li) and once on oxygen (O). To change the formula of lithium oxide (Li2O) to lithium peroxide (L2O2), place the cursor next to the symbol of oxygen in the input field and click once on oxygen (O).
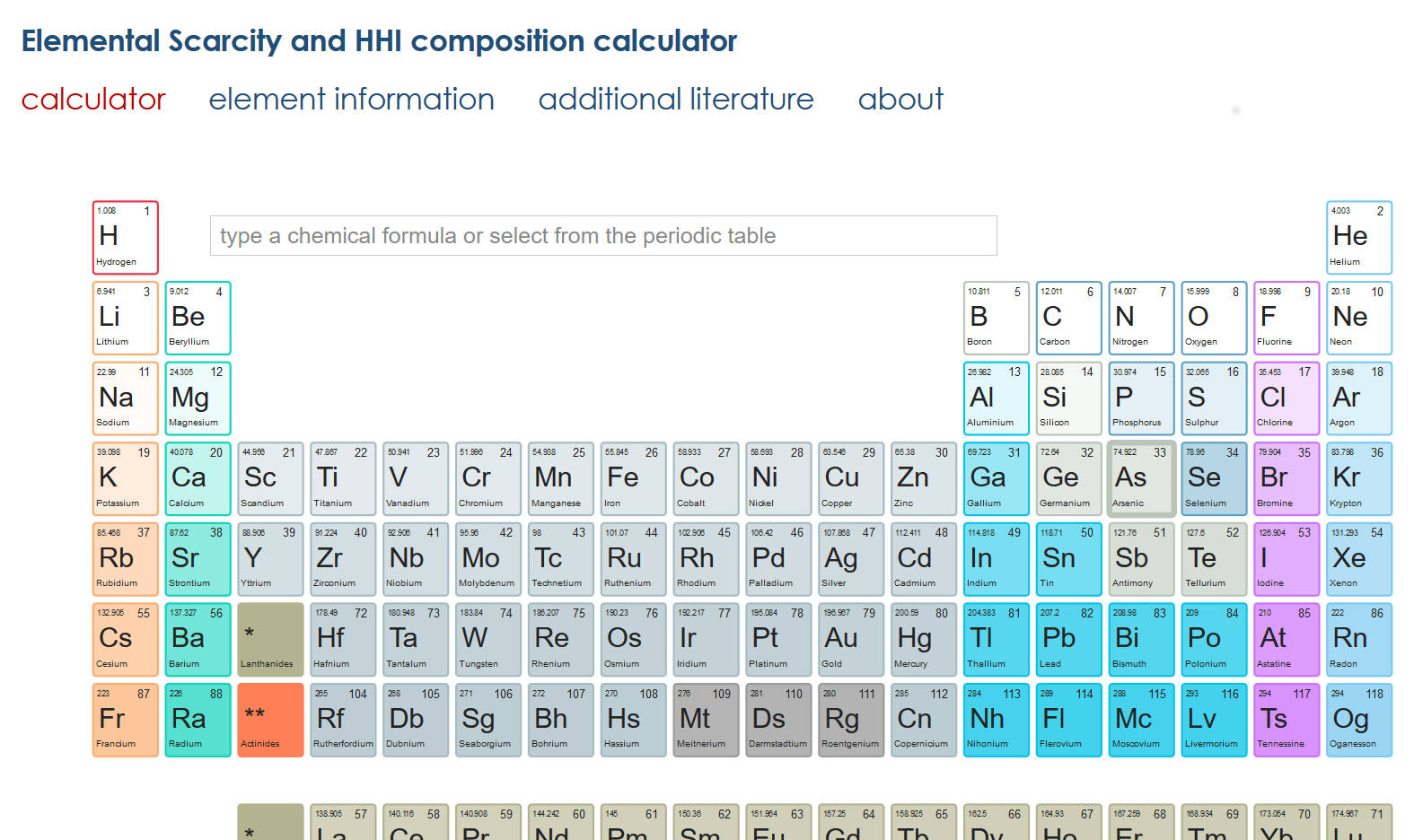
The scarcity and HHI data is displayed below the input box (Figure 2). When abundance, scarcity, or HHI values are not available for any of the compound elements, "N/A" is displayed in the corresponding field.
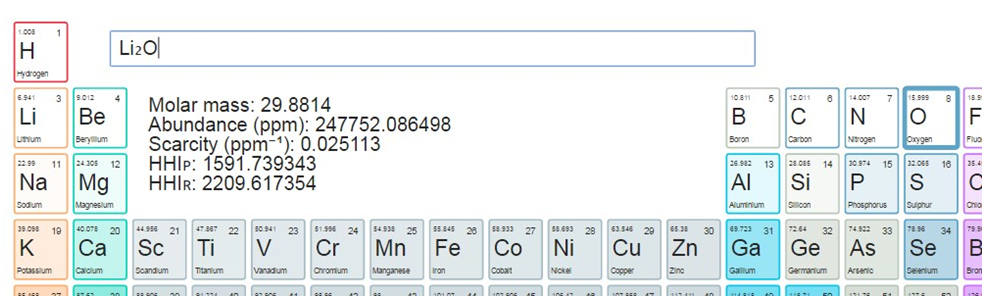
2. Supported chemical formula formats
The calculator supports chemical formulas containing:
- Chemical symbols
- Stoichiometric coefficients
- Charges: “+” and “-”
- Parentheses for repeating units: “(” and “)”
- Square brackets for complex salts: “[” and “]”
- Underscore (denoting subscript) in front of the stoichiometric coefficient: “_”
- Non-Stoichiometric values for the stoichiometric coefficient of elements and repeated units, e.g. 0.025, or 0.1.
Example of valid formulas:
- Na
- Na+
- Li2O
- Zn0.9975Al0.0025O1
- C12H22O11
- H(CO)(CHOH)5H
- NaOH
- Cr2O7
- Ca(OH)2
- Mg3(PO4)2
- ((((Pt)7)5))
- (Fe2)O3
- NH4[Cr(SCN)4(NH3)2]3
- (CH_3)_2CHOH
There is no limit to the number of elements in a formula.
3. Batch calculation
Calculation of scarcity and HHI values is also possible for lists of compounds. A list of compounds can be uploaded through the “Choose File” button under the periodic table keyboard. Separate compounds can be delimited with a newline and/or comma. Examples of valid input file formats:
Newline separated
Cr2O7
Ca(OH)2
Mg3(PO4)2Comma separated
Cr2O7,Ca(OH)2,Mg3(PO4)23.1. Output
When the calculation has finished, a “Save As” dialog will appear. The default name of the output file is “results.csv”. It is a comma-separated file with the following columns:
- Formula - compound/material formula as provided by the user
- Molar mass - the molar mass of the compound/material
- Abundance (ppm) - the crustal abundance of the compound/material in ppm based on the weight fraction of elements in the chemical formula
- Scarcity (1/ppm) - the effective scarcity of the compound/material in inverse ppm based on the weight fraction of elements in the chemical formula
- HHI (production) - the HHI production value of the compound/material based on the weight fraction of elements in the chemical formula
- HHI (reserves) - the HHI production value of the compound/material based on the weight fraction of elements in the chemical formula
- error_message - errors occurred during calculation are listed in this column. For example, errors in the parsing of the chemical formula or the input file. The message is "OK" if the calculation has been completed without errors.
The value in the abundance, scarcity and HHI columns is "N/A" when scarcity or HHI values are not available for an element of a compound/composition.
4. Element information
On this page the periodic table keyboard can be used to display information about each element:
- Atom number
- Molar mass
- Chemical symbol
- Element name
- Abundance
- Scarcity
- HHI (production)
- HHI (reserves)
Click on an element to display its information (Figure 3)
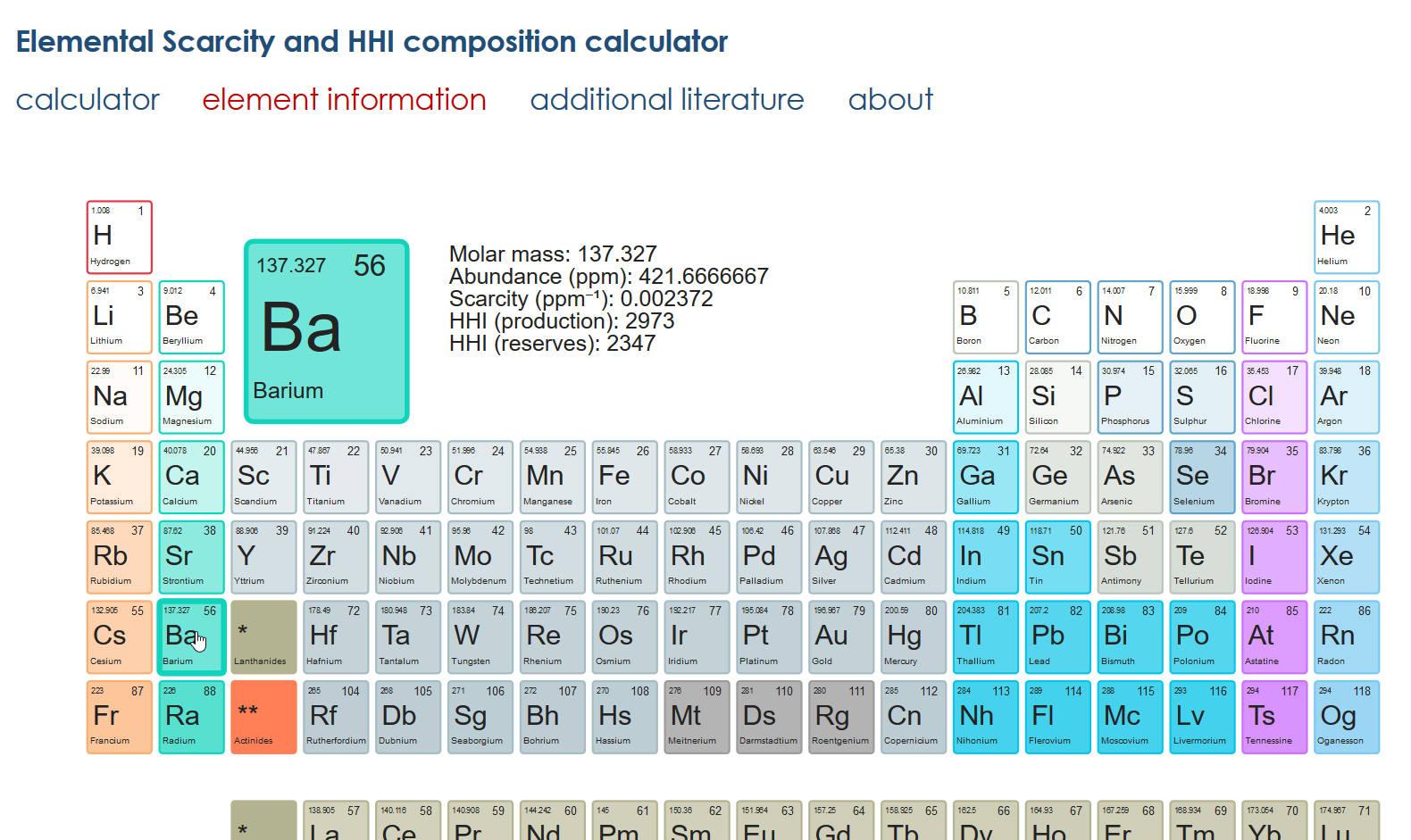
5. Plot
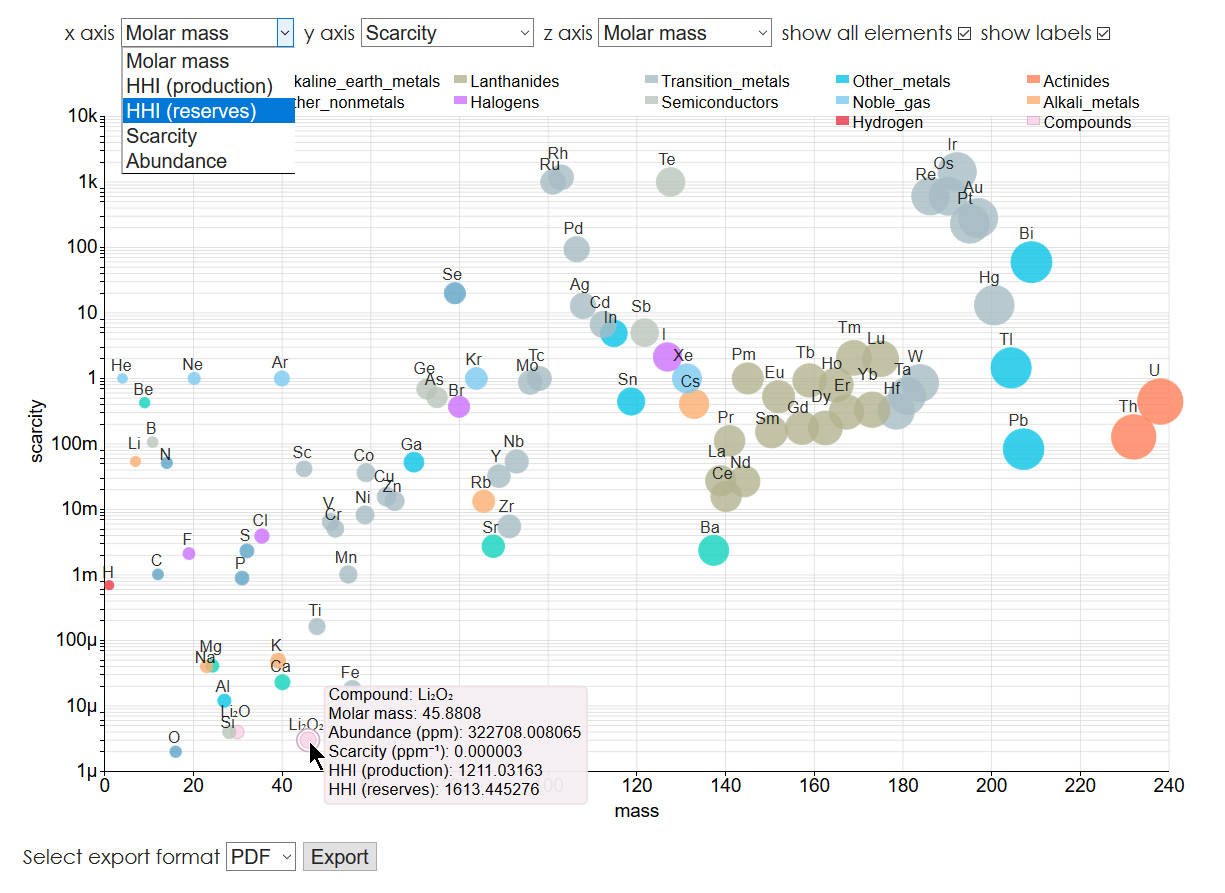
On this page compounds and compositions can be sent to a scatter plot situated under the periodic table keyboard (Figure 4, Figure 5).
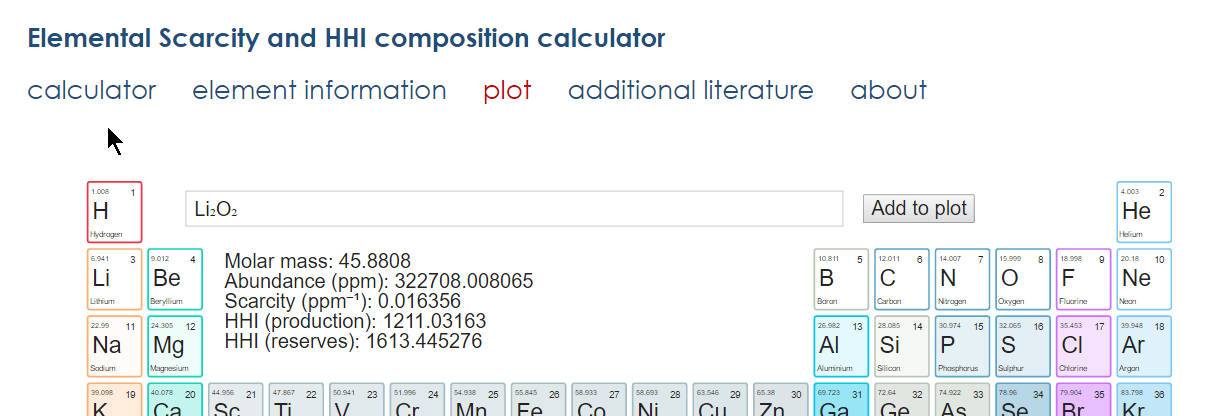
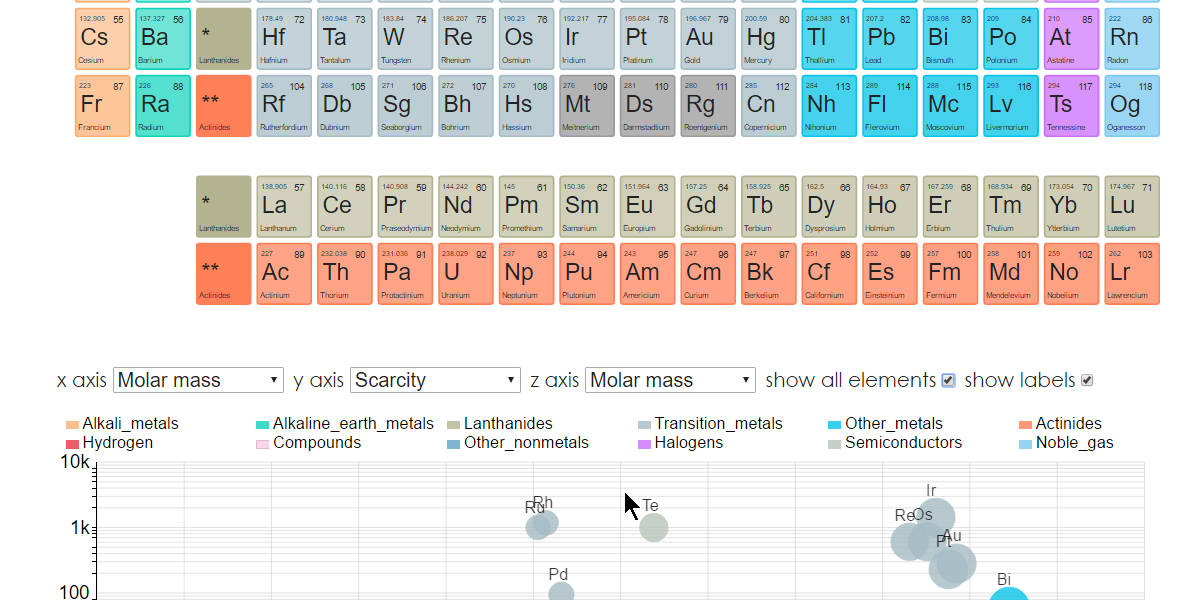
The plot has three dimensions - x, y, and z-axis, where the z-axis is represented by the size of the marker. By default, all chemical elements with scarcity or market concentration (HHI) information are loaded on the plot. The color of the markers is bound to the type of the element (Figure 6). Parameter selectors, display options, and a color legend are shown above the chart. The selectors allow the visual comparison of elements and compounds by any combination of parameters on the three axes:
- Molar mass
- HHI (production)
- HHI (reserves)
- Scarcity
- Abundance
The values for all these parameters are shown in the tooltip of each data point.
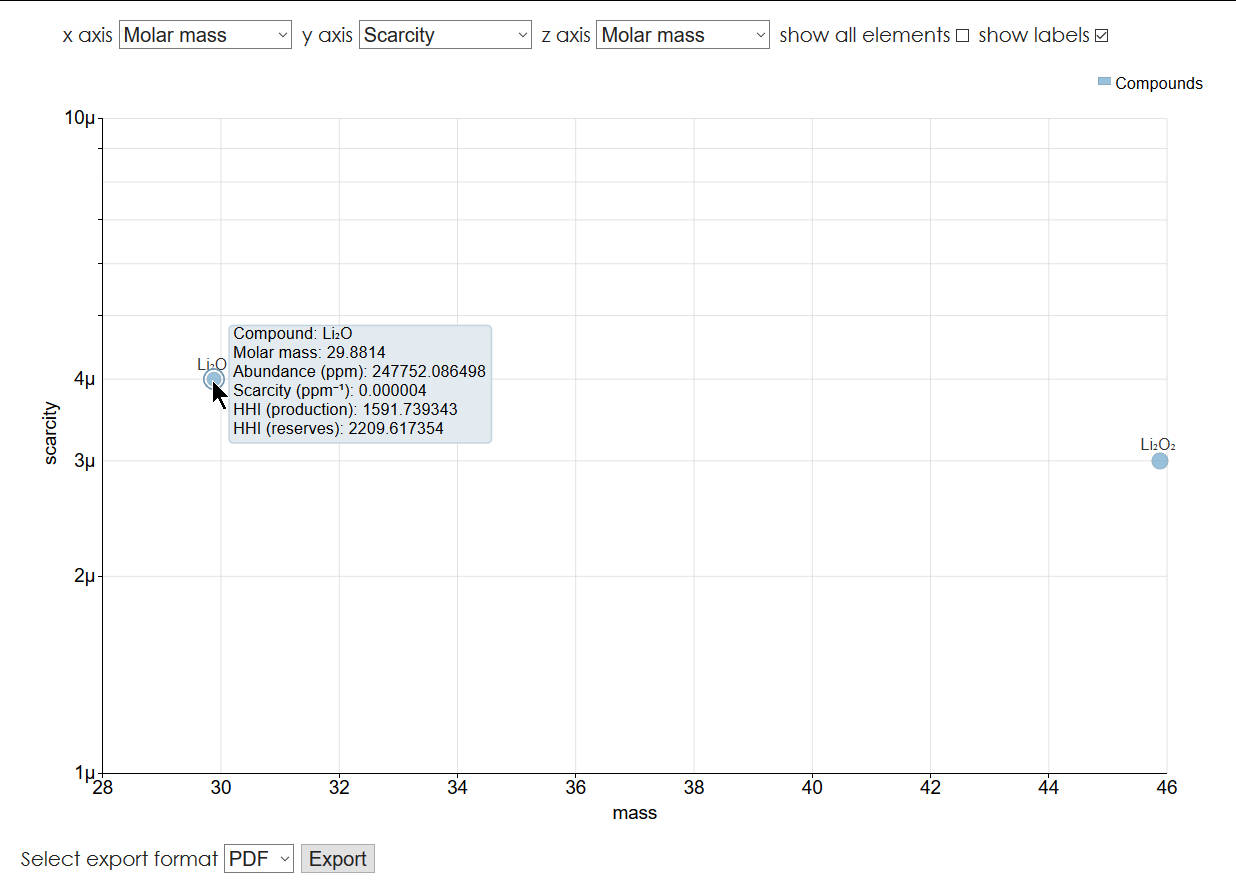
The z-axis has one additional parameter - “None”. It disables the z-axis binding and makes all data points appear with the same diameter.
If not needed, chemical elements can be removed from the plot through a checkbox in the upper right corner of the plot. When the parameter values require it, the axes are automatically switched to a logarithmic scale in order to properly display all data points. The units within one axis are displayed with metric prefixes - for example, μ is for micro- (10-6) and m for milli- (10-3) (Figure 6, Figure 7).
Under the graph, there is an export button with four format options: PDF, PNG, SVG, and EPS. When the image is ready, the download starts automatically. All settings of the plot affect the resulting images.
6. Additional literature
This page displays details and links to papers that have been used for the data and methods behind the Elemental Abundance Composition Calculator.
7. Supported browsers
- Chrome
- Firefox
- Safari
- Microsoft Edge 14+
- Internet Explorer 11
For more details, please refer to the original publication - DOI: 10.1007/s40192-017-0085-4